Introduction to Version Control
Thursday, September 26
Today we will…
- Review Key Feedback from Lab 4 & Challenge 4
- Discuss New Structure for Revisions
- New Material
- Version Control
- Setting-up Portfolio
- Forking the Final Portfolio Repository
- Cloning into RStudio
- Making a Small Change, Committing & Pushing
Lab 4 Common Mishaps
Q1: Who collected these data? When? Why? How?
Q4: Column titles of
2008and2018are not descriptive!- Creating column names that describe the values stored in those columns!
- The
names_prefix =argument topivot_wider()can help you make better column names! - DVS-6: I can create tables which make my summaries clear to the reader
Q4: Unless you specify
.groups = "drop"withinsummarize()your table still is grouped!group_by()+summarize()only drops the first group.- If you have two variables inside
group_by(), then the data will still be grouped by the second variable!
Q7: The data description contains important information!
mc_toddler– Aggregated weekly, full-time median price charged for Center-based Care for toddlers.mhi_2018– Median household income expressed in 2018 dollars.
Superseded Functions
PE-4: I can use modern tools when carrying out my analysis.
recode()from the dplyr package has been superseded for thecase_match()function.case_match()is the SQL cousin ofcase_when()
- Neither of these functions live in the forcats package which includes the tools we learned!
- Neither is
factor()! - Maybe try something from forcats!
- Neither is
Other “Big Picture” Code Feedback
I strongly recommend against nested functions, as they are difficult for people to understand what your code is doing. Having two lines is not less efficient and is more readable.
Non-Nested Functions
I strongly recommend against nested functions, as they are difficult for people to understand what your code is doing. Having two lines is not less efficient and is more readable.
Saving Objects That Aren’t Worth Saving
Challenge 3
DVS-2: I use plot modifications to make my visualizations clearer to the reader
- Facets ordered based on developmental stage not alphabetically.
- Ordering colors in the legend so they appear in the same order as the lines in the plot.
- Adding $ signs to axis labels.
- Not making people tilt their head to read your plot.
- Using meaningful labels (e.g., “Infant” not “mfcc_infant”).
Challenge 3
DVS-3: I show creativity in my visualizations
- Exploring different color themes
- Here is an incredible resource with extensive color themes: https://emilhvitfeldt.github.io/r-color-palettes/discrete.html
- paletter – multiple color palette packages in one place
Challenge 3
DVS-3: I show creativity in my visualizations
- Exploring different plot themes
- Personally, I like
theme_bw(), but you might like others! - Remember to keep major gridlines! They are important for readablity!
- Personally, I like
New Structure for Lab Revisions
Due to the time it is taking me to give feedback for the lab and challenge assignments, I need to find a new plan for revisions.
New Plan:
- Spend 45-minutes of class on Thursdays working on revisions with people around you, and discussing your revisions with me.
- Revisions will be graded as “Success” or “Growing” with no additional feedback provided.
- Additional feedback can be given during student hours!
Version Control
Version Control
A process of tracking changes to a file or set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions later.
Git vs GitHub

- A system for version control that manages a collection of files in a structured way.
- Uses the command line or a GUI.
- Git is local.

- A cloud-based service that lets you use git across many computers.
- Basic services are free, advanced services are paid (like RStudio!).
- GitHub is remote.
Why learn version control?
- GitHub provides a structured way for tracking changes to files over the course of a project.
- Think Google Docs or Dropbox history, but more structured and powerful!
GitHub makes it easy to have multiple people working on the same files at the same time.
You can host a URL of fun things (like the class text, these slides, the course website, etc.) with GitHub pages.
Preparatory Work
You were asked to complete the following steps before coming to class today:
- Create a GitHub account
- Introduce yourself to git (in RStudio)
- Generate a Personal Access Token (PAT)
- Store your PAT in RStudio
Using git and GitHub in RStudio
I’m going to guide you through how to interact with git and GitHub through RStudio. This is not the only way to do this! If you are comfortable with version control, feel free to use the tool that you like best.
Git Repositories
Git is based on repositories.
- Think of a repository (repo) as a directory (folder) for a single project.
- This directory will likely contain code, documentation, data, to do lists, etc. associated with the project.

Actions in Git
Forking a Repo
Make your own copy of a project.
- The original repository is like the main version of a project.
- When you fork it, you make your own copy of that project under your own account.
- You can freely make changes, test ideas, or add new features in your fork.
- The original project stays untouched.
Your Turn
Navigate the the Final Portfolio repository linked on Canvas.
Create your own fork of that repository.
Cloning a Repo
Download the project onto your computer.
- A repository (repo) lives online.
- When you clone it, you make a local copy on your computer.
- All the project files, history, and branches come with it.
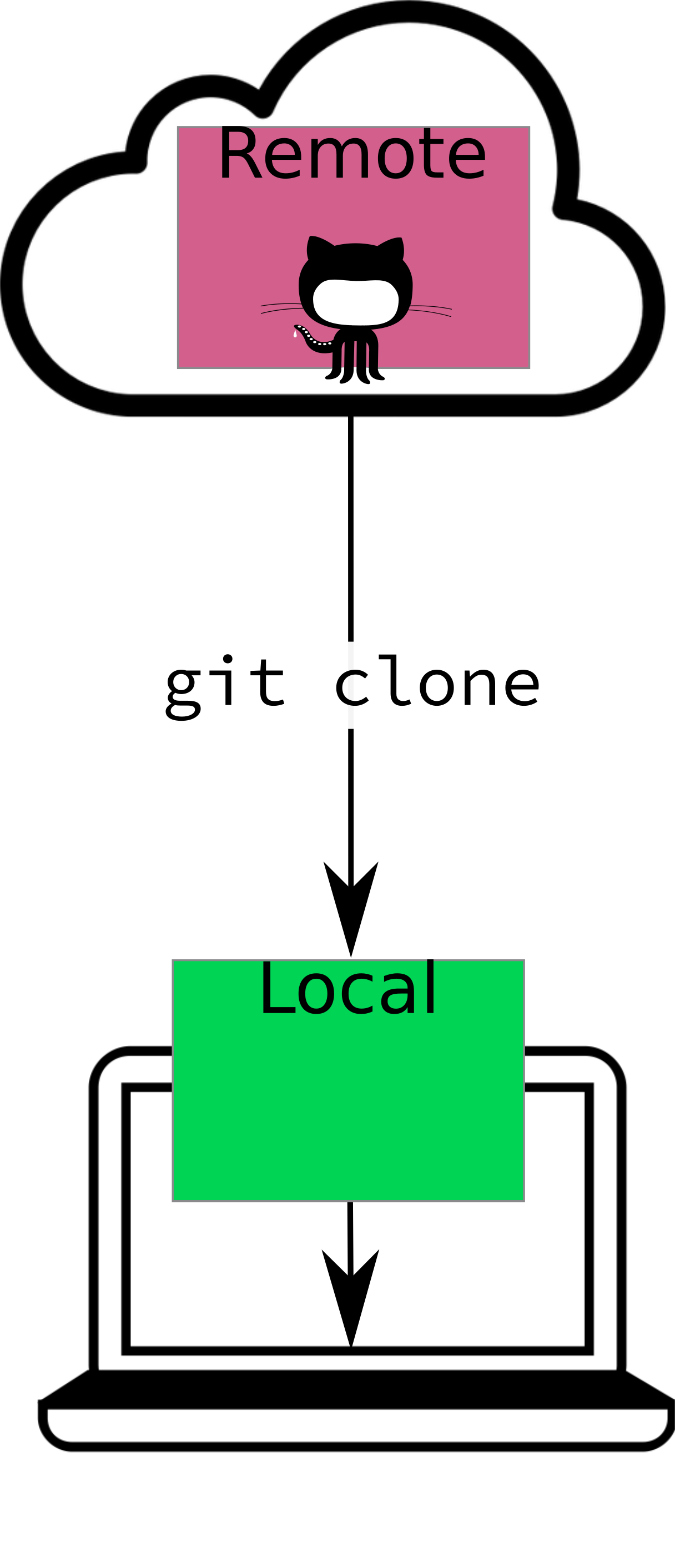
Your Turn
Navigate to your fork of the Final Project Portfolio repository – the one you own!
Follow the instructions posted on Canvas to clone that repository into RStudio.
Committing Changes
Record any changes you’ve made.
- Whenever you make changes you can “commit” those changes to record them permanently in your project’s history.
- You also provide a commit message – describing what changes you made.
- The log of these changes is called your commit history.
- You can always go back to old copies!

Commit Tips
- Commit small blocks of changes.
- Commit every time you accomplish a small task (e.g., one learning target).
- With frequent commits, its easier to find the issue if / when you mess up!
- Use short, but informative commit messages.
- You’ll end up with a set of bite-sized changes (with description) to serve as a record of what you’ve done.
Your Turn
Dr. Theobold will live code this process!
Pushing Changes
Send your commit to the remote repository so others can see and access them.
- Send the changes you’ve saved in your commit to GitHub.
- No one else can see the changes you’ve made locally unless you push them!
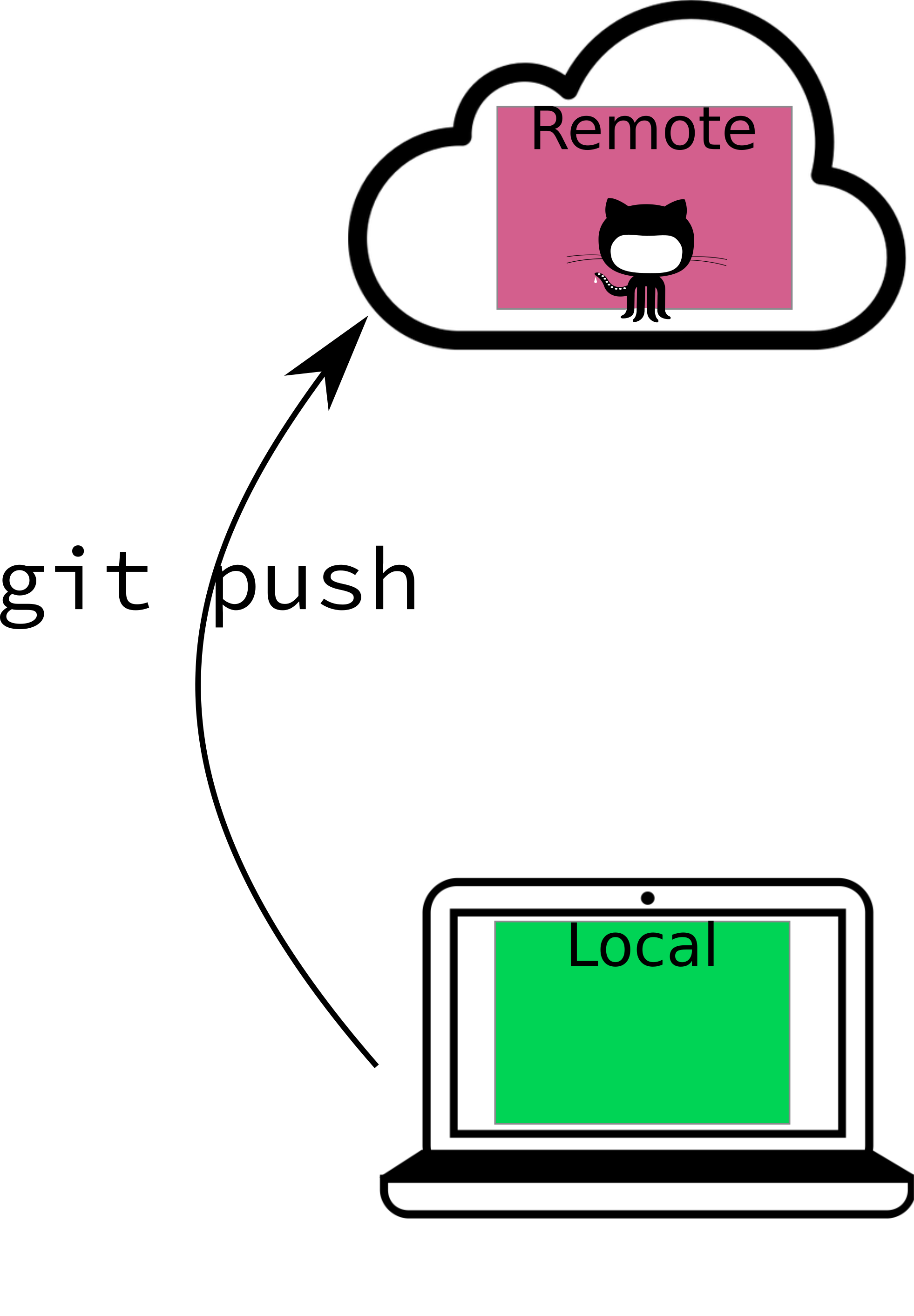
Your Turn
Dr. Theobold will live code this process!
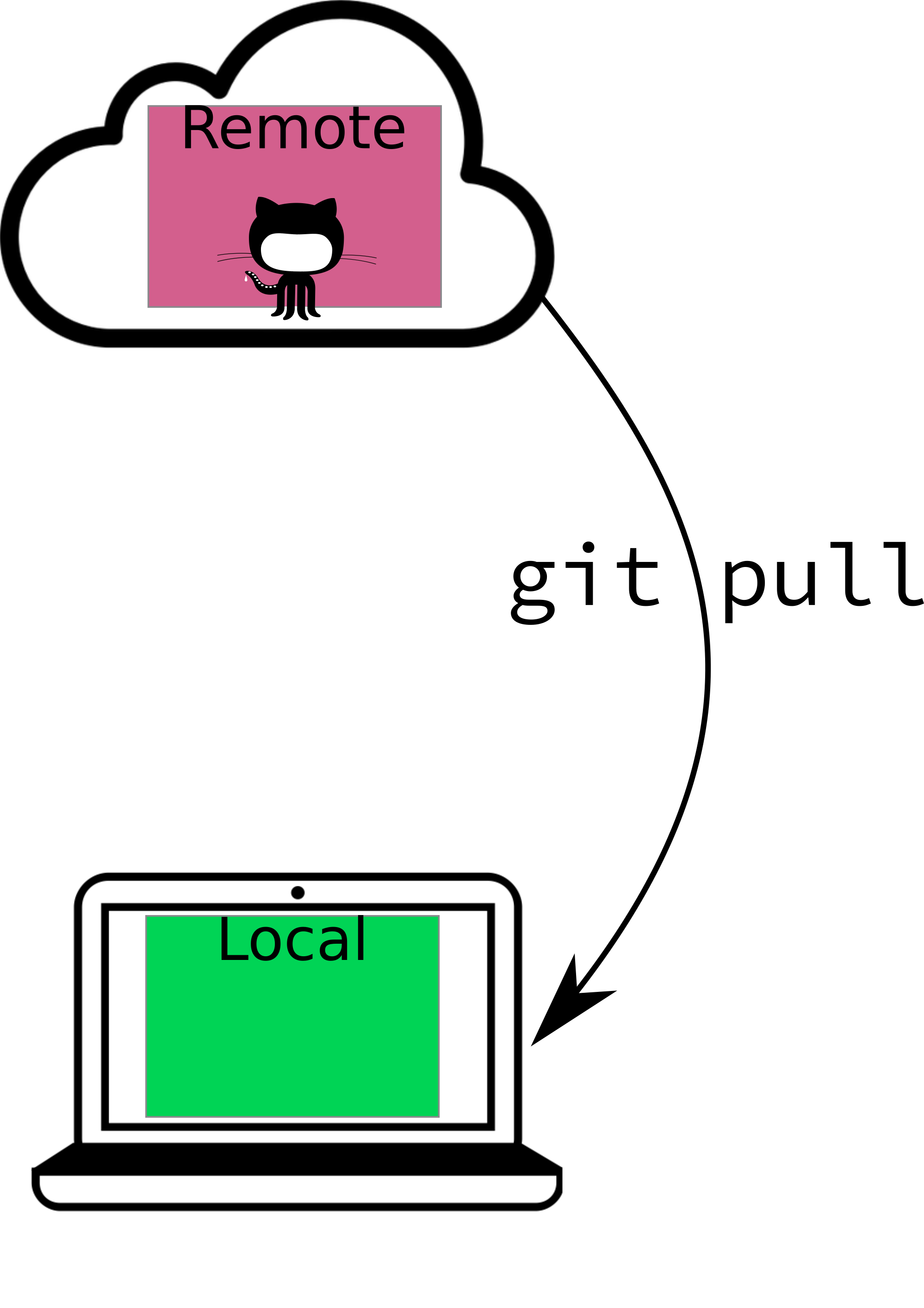
Pulling Changes
Download the latest changes from the remote repository into your local copy.
- Your updates are saved online when you commit and push.
- To see those new edits in your offline copy, you have to pull them down.
Only relevant if you are working on two computers!
If this is you, keeping both local versions up to date will be important!
Workflow
- Pull the repo to make sure you have the most up to date version (especially if you are working on different computers).
- Make some changes locally.
- Commit the changes.
- Push your changes to GitHub.
Final Portfolio
Resources Available to You
- Handout on what learning targets we’ve covered thus far.
- You shouldn’t have code for the ones that aren’t listed!
- Examples of how to select a code example that satisfies multiple learning targets.
- This can save you time!
- Examples of portfolios from previous students
- Please note the difference between the grade they suggested and the grade they were assigned.
To do…
- Lab 4 revisions due Friday at 11:59pm
- Final Portfolio due Sunday at 11:59pm